AQA A-Level Biology
-
Sample content (FREE TO VIEW)5 Lessons
-
Biological Molecules10 Lessons
-
Cells6 Lessons
-
Organisms exchange substances with their environment5 Lessons
-
Genetic information, variation and relationships between organisms7 Lessons
-
Energy transfers in and between organisms4 Lessons
-
Organisms respond to changes in their internal and external environments9 Lessons
-
? Survival and response
-
? Receptors
-
? Control of Heart Rate
-
⚡ Nerve Impulses
-
? Synaptic Transmission
-
?♂️ Skeletal muscles are stimulated to contract by nerves and act as effectors
-
✋ Principles of homeostasis and negative feedback
-
?️ Control of Blood Glucose Concentration
-
⚖️ Control of blood water potential
-
? Survival and response
-
Genetics, populations, evolution and ecosystems4 Lessons
-
The control of gene expression8 Lessons
-
? Alteration of the sequence of bases in DNA can alter the structure of proteins
-
? Most of a Cell's DNA is not Translated
-
? Regulation of Transcription and Translation
-
?⚕️ Gene expression and cancer
-
? Using genome projects
-
? Recombinant DNA Technology
-
? Differences in DNA between individuals of the same species can be exploited for identification and diagnosis of heritable conditions
-
?️♂️ Genetic Fingerprinting
-
? Alteration of the sequence of bases in DNA can alter the structure of proteins
? Lipids (FREE SAMPLE)
The A Level Biologist - Your Hub February 12, 2020
Membranes are made of phospholipids , which are made of lipids . Lipids are the stuff of oils, fats and waxes. Unlike proteins and carbohydrates, lipids are not polymers. Lipids which store energy are triglycerides , while those which form membranes are phospholipids. Triglycerides are formed by a molecule of glycerol with three fatty acids attached. The reaction which results in triglycerides is condensation .
Glycerol (green) + 3x fatty acids (red) The fatty acids can be simplified in drawing:
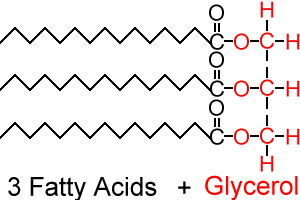
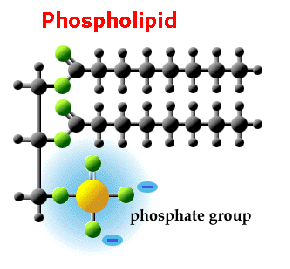
The bonds formed (C-O) are called ester bonds . Fatty acids can be saturated or unsaturated (monounsaturated; polyunsaturated). Saturated fatty acids have all their carbon (C) atoms linked to hydrogen (H) atoms, hence saturated with hydrogen . If there is a carbon atom with a double bond to its neighbour carbon atom, then it will only have one bond to a hydrogen atom, hence it is unsaturated. If there is one double bond present, the fatty acid is monounsaturated . If there are multiple double bonds present, the fatty acid is polyunsaturated . In phospholipids one of the fatty acids is replaced by a phosphate group .
The test for lipids is the emulsion test . This test takes advantage of the property of lipids of not dissolving in water, but dissolving in ethanol (alcohol). You dissolve the sample into ethanol by shaking, then pour it into water. If milky white droplets are formed, the sample is positive for lipids.
