AQA A-Level Biology
-
Sample content (FREE TO VIEW)5 Lessons
-
Biological Molecules10 Lessons
-
Cells6 Lessons
-
Organisms exchange substances with their environment5 Lessons
-
Genetic information, variation and relationships between organisms7 Lessons
-
Energy transfers in and between organisms4 Lessons
-
Organisms respond to changes in their internal and external environments9 Lessons
-
? Survival and response
-
? Receptors
-
? Control of Heart Rate
-
⚡ Nerve Impulses
-
? Synaptic Transmission
-
?♂️ Skeletal muscles are stimulated to contract by nerves and act as effectors
-
✋ Principles of homeostasis and negative feedback
-
?️ Control of Blood Glucose Concentration
-
⚖️ Control of blood water potential
-
? Survival and response
-
Genetics, populations, evolution and ecosystems4 Lessons
-
The control of gene expression8 Lessons
-
? Alteration of the sequence of bases in DNA can alter the structure of proteins
-
? Most of a Cell's DNA is not Translated
-
? Regulation of Transcription and Translation
-
?⚕️ Gene expression and cancer
-
? Using genome projects
-
? Recombinant DNA Technology
-
? Differences in DNA between individuals of the same species can be exploited for identification and diagnosis of heritable conditions
-
?️♂️ Genetic Fingerprinting
-
? Alteration of the sequence of bases in DNA can alter the structure of proteins
? Monomers and Polymers (FREE SAMPLE)
The A Level Biologist - Your Hub February 12, 2020
Life in its ecosystems, species and organisms has been expressed, and continues to do so, in a great variety of ways.

Yet on the biochemical level, deep down into the tissue, cells and microscopic components that make up these living things, the basic building blocks are the same! A bit like how everything is just made up of atoms or quarks or just empty space really but it somehow ends up looking really interesting to us.
Some of these basic building blocks are called monomers (“single part”, Greek) and join together to create bigger molecules called polymers (“many parts”? I don’t know, I’m making this up).
Examples of monomers that we’ll go into more depth in later topics include monosaccharides such as glucose, amino acids such as methionine, and nucleotides which make up DNA.
How can monomers create a polymer? The types of chemical reactions yielding bonds to enable this to happen are many. One of the key ones is called condensation. It is a joining reaction and releases water in the process.
Its reverse reaction uses up water and breaks up the bond. You might have come across it before – hydrolysis (breaking water? breaking with water?).
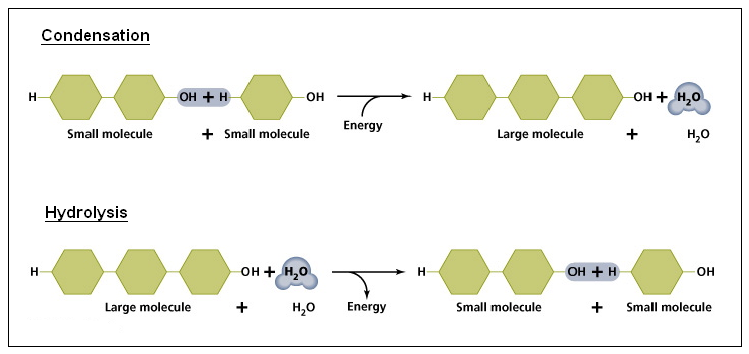
In this context the monomers are like standard lego pieces that can be joined any way to build bigger things with – notice the hydrogen (H) and hydroxyl (OH) groups on either end of each small molecule. That’s where further molecules can join up and grow really large molecules.
Ok byeeee
