Back to Course
Edexcel A2-Level Biology
0% Complete
0/0 Steps
-
Sample content (FREE TO VIEW)3 Lessons
-
5. Energy for Biological Processes7 Lessons
-
6. Microbiology and Pathogens7 Lessons
-
7. Modern Genetics4 Lessons
-
8. Origins of Genetic Variation3 Lessons
-
9. Control Systems9 Lessons
-
?? Homeostasis
-
? Chemical Control in Mammals
-
? Chemical Control in Plants
-
? Structure and function of the mammalian nervous system
-
? Nervous transmission
-
? Effects of drugs on the nervous system
-
?️ Detection of light by mammals
-
? Control of heart rate in mammals
-
⚖️ Osmoregulation and temperature regulation
-
?? Homeostasis
-
10. Ecosystems4 Lessons
Section 1,
Lesson 2
In Progress
⚡ Glycolysis (FREE TO VIEW)
The A Level Biologist - Your Hub February 25, 2020
Section Progress
0% Complete
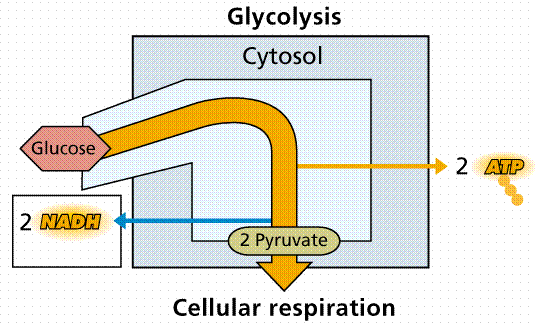
1. Glycolysis
Glycolysis literally means a glucose molecule is hydrolysed (broken down) by water into two. I bet you’re itching to find out what it’s broken down into. Glad you asked. It’s broken down into these molecules called pyruvate.
It didn’t even to go far, and we’ve already got a net of 2 ATP molecules produced! Another by-product of this reaction is NADH (reduced NAD – the addition of a proton/H atom/electron constitutes a reduction, whereas the loss of either species constitutes an oxidation) of which 2 are obtained.